What Is Steel Grating Strength and Why Does It Matter?
Steel grating strength refers to the ability of a grating panel to resist loads without permanent deformation or structural failure. It is a crucial parameter because steel gratings are widely used in heavy-duty industrial walkways, platforms, work areas, loading zones, and architectural features such as facades and shading systems.
In both industrial and architectural settings—such as those served by
Huijin Metal Meshes—steel gratings must safely support static loads, dynamic loads, impact forces, and human foot traffic.
Grating strength is influenced primarily by:
Bearing bar size (depth and thickness)
Bar spacing
Material type (carbon steel, stainless steel, galvanized steel)
Load direction relative to bearing bars
Span length
Load distribution
Manufacturing method (welded, swaged, press-locked)
Proper evaluation ensures that structures stay safe, functional, and compliant with engineering standards such as ANSI/NAAMM MBG 531, EN ISO standards, and local building codes.
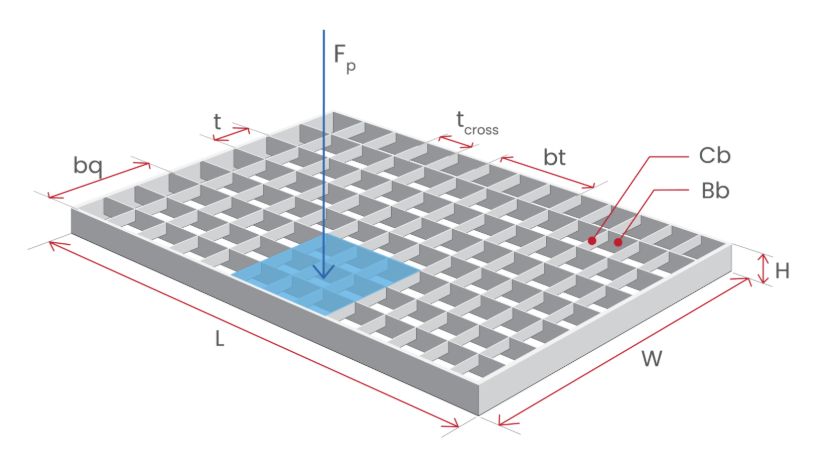
How Do Bearing Bars Determine Steel Grating Strength?
The bearing bars are the primary load-carrying elements in any grating system. They run parallel across the span and take the applied loads directly. Therefore, their size and spacing are the most significant factors in steel grating strength.
Bearing Bar Depth
Greater bar depth increases the section modulus, enabling the bar to resist bending more effectively.
Typical depths range from:
Bearing Bar Thickness
Thicker bars boost strength but also add weight. Common thicknesses include:
Bearing Bar Spacing
Narrow spacing increases strength and reduces deflection. Standard spacings:
Closer spacing improves steel grating strength and provides better support for small equipment wheels or concentrated loads.
How Does Span Length Influence Steel Grating Strength?
Span is the distance between supports. As a rule, the longer the span, the lower the steel grating strength because bending moments increase exponentially.
Maximum Allowable Span
Engineers use span tables to determine which bearing bar size is appropriate for expected loads. For example:
Span Direction
Loads must be applied perpendicular to bearing bars.
If loads are applied parallel to bars, the grating loses almost all its strength.
Deflection Limits
Most standards limit maximum deflection to:
Deflection control is essential for comfort, safety, and long-term structural performance.
What Types of Loads Affect Steel Grating Strength?
Different environments impose different loading conditions, each affecting the steel grating strength calculation.
Uniformly Distributed Load (UDL)
Common in walkways, industrial platforms, and mezzanines.
Example: 5 kN/m² load spread evenly.
Concentrated Loads
A single force applied at one point or distributed over a small area, such as:
Impact Loads
Forklifts, tool drops, vibration machinery, or vehicle movements create dynamic forces.
Engineers add impact factors (e.g., +20–50%) to ensure safety.
Vehicular Loads
For truck-rated steel gratings, designers must use formulas similar to bridge deck calculations, considering axle loads and wheel distribution.
Understanding load types is essential for accurate calculation and safe application.
How Do Engineers Calculate Bending Stress and Deflection?
To determine steel grating strength, engineers rely on beam theory formulas. Each bearing bar acts like a small beam.
Bending Stress Calculation
Where:
Bending stress must be below the allowable stress of the steel material used.
Deflection Calculation
Where:
Allowable Stress and Safety Factors
Typical allowable stresses:
Carbon steel: 145 MPa
Stainless steel: 175 MPa
Safety factors of 1.5–2.0 are commonly applied depending on environment and regulations.
How Are Load Ratings Assigned to Steel Grating?
Load ratings indicate how much weight a grating can safely support. Engineers classify gratings into:
Light-Duty Gratings
Pedestrian load
Maintenance walkways
HVAC service access
Medium-Duty Gratings
Industrial platforms
Conveyor access
Storage mezzanines
Heavy-Duty Gratings
Forklift traffic
Mining platforms
Vehicle loading zones
Load ratings are derived through the combination of:
Material strength
Bearing bar geometry
Span
Safety factor
Load distribution type
These factors combine to determine the published load tables used by engineers and designers.
How Do Material Types Affect Steel Grating Strength?
Carbon Steel
Most common due to high strength and cost-effective performance.
Yield strength typically 235–275 MPa.
Stainless Steel
Higher resistance to corrosion; often used in chemical plants, marine environments, or architecture.
Yield strength around 304–310 MPa varieties.
Galvanized Steel
Structural performance similar to carbon steel but with improved corrosion resistance.
Material selection affects long-term performance but also influences the steel grating strength calculation because each material has different mechanical properties.
How Do Manufacturing Methods Influence Steel Grating Strength?
Welded Steel Grating
Most common and strongest manufacturing method.
Welding fuses bearing bars and cross bars permanently, creating excellent shear resistance.
Press-Locked Grating
Bearing and cross bars are mechanically locked together.
Provides a clean architectural appearance.
Swaged Grating
Cross bars are pushed into pre-punched holes under pressure.
Suitable for aluminum or lighter steel panels.
Manufacturing affects strength, durability, and recommended load ratings.
How Do Standards Help Engineers Calculate Steel Grating Strength?
The steel grating industry relies on international standards to ensure uniformity and safety.
Key Standards Include:
NAAMM MBG 531 (North American standard)
ANSI/ASCE codes
EN ISO 14122 for industrial walkways
ASTM A123 / A36 material standards
These standards provide:
Material properties
Maximum deflection limits
Load classification
Fabrication guidelines
Testing methods
Engineers reference these documents extensively when determining steel grating strength and selecting appropriate specifications for each project environment.
How Do You Select the Right Steel Grating Based on Strength Requirements?
Selection depends on both the strength and application environment.
Determine Load Type
Pedestrian? Industrial? Vehicular? Impact?
Calculate Required Bar Size
Use span/load tables to match bearing bar size to expected loads.
Check Deflection Limits
Ensure the grating does not exceed allowable deflection.
Evaluate Environmental Conditions
For corrosive or aesthetic environments, stainless steel or special coatings may be needed.
Confirm Compliance with Standards
Always verify that chosen specifications meet local and international regulations.
Through these steps, even architectural designers using materials like
Huijin Metal Meshes can safely integrate grating systems into facades, shading structures, or structural platforms.
What Are Common Mistakes in Evaluating Steel Grating Strength?
Ignoring Load Direction
Applying load parallel to bearing bars drastically reduces strength.
Misjudging Span Length
Even a slight increase in span length significantly reduces load capacity.
Overlooking Concentrated Loads
Heavy point loads often govern the design instead of uniform loads.
Using Non-Standard Materials
Improper steel grade affects allowable stress.
Installing Grating Incorrectly
Lack of proper fastening or support reduces actual steel grating strength.
Avoiding these mistakes is essential for safety and material optimization.
Conclusion
Calculating steel grating strength requires a detailed understanding of bearing bar geometry, load types, span behavior, material properties, and safety standards. By applying established engineering formulas and evaluation methods, designers can ensure that steel gratings perform reliably in industrial and architectural environments. Whether for walkways, platforms, facades, or enclosures, proper load rating and strength calculation are essential for long-term durability and safety.
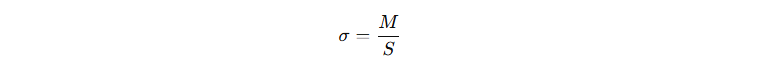
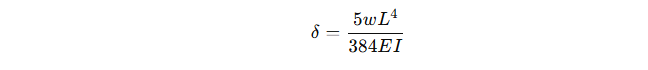
Comments