Grating spacing is a critical factor in determining the performance, safety, and suitability of metal meshes like Huijin’s galvanized safety grating for various applications. Whether used in industrial settings such as walkways, platforms, and filters or in architectural designs like building facades and ceiling systems, understanding how to calculate this spacing ensures the grating meets structural and aesthetic requirements. This article delves into the technical aspects of grating spacing, offering valuable knowledge for engineers, architects, and designers working with galvanized safety grating.
What Is Grating Spacing and Why Does It Matter?
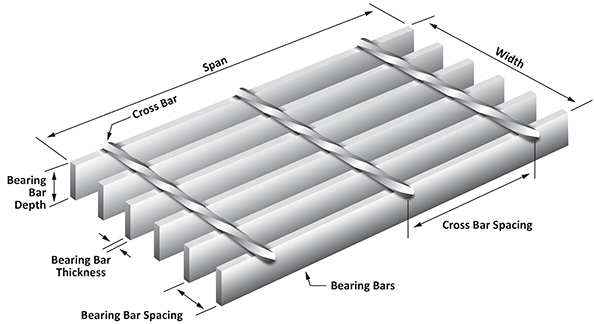
Grating spacing refers to the distance between the bars or openings in a grating panel, typically measured as the center-to-center distance between load-bearing bars or the clear opening between them. For galvanized safety grating, this spacing directly impacts its load-carrying capacity, safety features, and filtration efficiency. In industrial applications like construction sites or platforms, proper spacing prevents objects from falling through while supporting heavy loads. In architectural uses, such as fences or decorative facades, it influences both functionality and visual appeal.
The importance of spacing lies in its ability to balance strength, safety, and practicality. For instance, Huijin metal meshes, including galvanized safety grating, are designed to meet diverse needs—whether it’s ensuring worker safety on a walkway or enhancing a building’s exterior with a stylish facade. Calculating spacing accurately ensures the grating performs as intended without compromising its purpose.
Several variables must be considered when determining the spacing for galvanized safety grating. These factors ensure the grating aligns with its intended use, whether in industrial enclosures or architectural ceiling systems.
Load Requirements: The weight the grating must support is a primary consideration. For industrial walkways or platforms, galvanized safety grating must withstand heavy machinery or foot traffic. Smaller spacing between bars increases load capacity, while wider spacing suits lighter loads, such as decorative fences.
Safety Standards: In applications like construction sites or shelves, spacing must comply with safety regulations. For example, OSHA guidelines often recommend a maximum clear opening to prevent tools or feet from slipping through galvanized safety grating on walkways.
Material and Coating: Galvanized safety grating, coated with zinc to resist corrosion, is ideal for harsh environments. The thickness and strength of the material influence how wide the spacing can be without compromising durability.
Application-Specific Needs: For filtering in industrial settings, spacing determines what particles pass through. In architectural facades, it affects light and air penetration, contributing to both design and energy efficiency.
By evaluating these factors, designers can tailor the spacing of galvanized safety grating to suit Huijin’s versatile product applications.
How Do You Calculate Grating Spacing Step-by-Step?
Calculating grating spacing involves a systematic approach that combines engineering principles with practical considerations. Below is a step-by-step guide to determining the spacing for galvanized safety grating:
Define the Load and Span: Start by identifying the maximum load (e.g., weight per square meter) and the span (distance between supports). For a walkway made of galvanized safety grating, this might be the weight of workers and equipment over a specific length.
Select Bar Dimensions: Choose the size and thickness of the load-bearing bars. Thicker bars in galvanized safety grating allow for wider spacing while maintaining strength, which is crucial for industrial platforms or construction sites.
Determine Allowable Deflection: Deflection, or the degree of bending under load, must stay within acceptable limits (e.g., L/240, where L is the span length). This ensures the galvanized safety grating remains stable and safe for use.
Calculate Spacing Using Formulas: Use structural engineering formulas to find the optimal spacing. For example, the maximum spacing (S) can be estimated based on the bar’s moment of inertia (I), the applied load (W), and the material’s modulus of elasticity (E):
Formula: S = √(k * I * E / W), where k is a constant based on boundary conditions.
This calculation ensures the spacing supports the load without excessive deflection.
Adjust for Safety and Functionality: Cross-check the calculated spacing against safety standards or application needs. For instance, in galvanized safety grating used as a filter, spacing might be reduced to trap smaller particles, while in a facade, it might be adjusted for aesthetic symmetry.
Test and Validate: Once calculated, prototype testing or software simulations can confirm the spacing works for the intended purpose, whether it’s a shelf, walkway, or decorative ceiling system.
This methodical process ensures galvanized safety grating meets the demands of Huijin’s industrial and architectural applications.
The spacing of galvanized safety grating has a direct impact on its performance across different scenarios. In industrial settings, such as enclosures or construction walkways, tighter spacing enhances slip resistance and prevents small objects from falling through, aligning with safety priorities. For example, a platform with closely spaced bars can support heavy machinery while protecting workers below.
In architectural uses, spacing influences both form and function. A building facade made with galvanized safety grating might feature wider spacing to allow natural light and ventilation, enhancing energy efficiency while maintaining a modern aesthetic. Similarly, in ceiling systems or fences, spacing can create patterns that elevate the design without sacrificing structural integrity.
The galvanization process itself—coating the steel with zinc—ensures the grating withstands environmental wear, making it a reliable choice regardless of spacing. This durability is why Huijin’s galvanized safety grating excels in diverse conditions, from humid industrial sites to exposed architectural exteriors.
Practical Examples of Grating Spacing in Action
To illustrate, consider an industrial walkway using galvanized safety grating. If the span is 1.5 meters and the load is 500 kg/m², engineers might calculate a spacing of 30 mm between bars to limit deflection and meet safety codes. In contrast, a decorative fence for a building facade might use 50 mm spacing to balance visibility, airflow, and style, leveraging the corrosion resistance of galvanization for long-term performance.
In filtering applications, such as those in Huijin’s industrial portfolio, spacing might shrink to 10 mm or less, depending on the particle size being targeted. These examples show how adaptable galvanized safety grating can be when spacing is calculated thoughtfully.
Tips for Optimizing Grating Spacing
Consult Load Tables: Manufacturers like Huijin often provide load tables for galvanized safety grating, simplifying spacing decisions based on span and weight.
Use Design Software: Tools like AutoCAD or structural analysis programs can refine calculations for complex projects.
Consider Maintenance: Wider spacing in galvanized safety grating reduces debris buildup, easing cleaning in industrial environments.
Balance Cost and Performance: Tighter spacing increases material use, so optimize based on budget and needs.
By applying these tips, users can maximize the benefits of
galvanized safety grating in both industrial and architectural contexts.
Conclusion
Calculating grating spacing for galvanized safety grating is a blend of science and practicality, tailored to the demands of industrial platforms, walkways, filters, or architectural facades and fences. By understanding load requirements, safety standards, and application goals, designers can ensure
Huijin’s metal meshes perform reliably and efficiently. This knowledge empowers professionals to create safer, more functional, and visually appealing solutions using galvanized safety grating.
Comments