Introduction: The Importance of Oxidation Prevention in Reflow Soldering
In advanced electronic manufacturing, especially in the packaging of power semiconductors and IGBT modules, oxidation is one of the major threats to bonding reliability. During reflow soldering, surfaces of metals such as copper and silver can easily oxidize when exposed to heat and air. These oxides reduce solder wetting, increase contact resistance, and lead to poor mechanical and electrical connections.
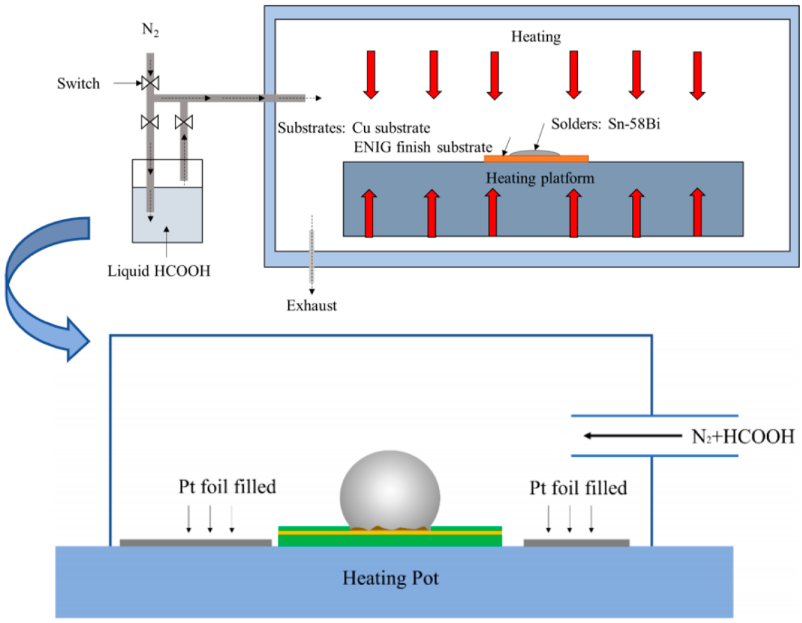
To counteract these problems, manufacturers increasingly focus on oxidation prevention strategies. One effective approach is using a controlled atmosphere during soldering. Among various methods, formic acid vapor stands out for its high efficiency in reducing metal oxides while maintaining compatibility with modern vacuum reflow systems.
What is Formic Acid and Why is it Used in Soldering?
Formic acid (HCOOH) is a colorless, organic compound with reducing properties. When used in reflow soldering, especially in a vacuum or inert atmosphere, formic acid acts as a chemical cleaning agent. It reacts with surface oxides on the metal, converting them into volatile compounds or metallic states that no longer interfere with solder bonding.
Its ability to provide active oxidation prevention at relatively low temperatures makes it an ideal flux substitute in fluxless or low-residue soldering applications. Moreover, it leaves minimal residue, reducing post-soldering cleaning steps.
How Formic Acid Achieves Oxidation Prevention
The oxidation prevention mechanism of formic acid is rooted in redox chemistry. Here’s how it works:
Surface Oxide Reduction:
When formic acid vapor contacts oxidized metal surfaces like CuO or SnO₂ under heat, it reduces these oxides to their pure metallic form:
Example reaction:
CuO + HCOOH → Cu + CO₂ + H₂O
Volatile By-Products:
The by-products of this reaction, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor, are easily removed in a vacuum environment, leaving a clean metal surface ideal for soldering.
Selective Reactivity:
Formic acid is particularly effective on copper, nickel, and tin oxides, which are commonly found in semiconductor and power device interconnects.
This active oxidation prevention process ensures improved solder joint reliability, better wetting, and lower void formation—factors that are essential in high-power and high-frequency devices.
Benefits of Oxidation Prevention with Formic Acid Atmosphere
Using a formic acid atmosphere for oxidation prevention during vacuum reflow soldering provides several key benefits:
Improved Solderability:
Oxide-free surfaces enhance solder wetting, ensuring strong metallurgical bonds.
Void-Free Packaging:
Clean surfaces minimize voids at the interface, which is critical for thermal and electrical conductivity in power modules.
Reduced Flux Dependency:
Eliminates or reduces the need for traditional fluxes, leading to cleaner processes with less residue.
Lower Defect Rates:
By preventing oxidation-related defects, yield rates in semiconductor packaging are improved.
Enhanced Reliability:
Long-term performance of the devices is enhanced due to consistent interfacial quality.
Where is Formic Acid-Based Oxidation Prevention Used?
This technique is widely applied in high-end electronics manufacturing, particularly in sectors requiring high-reliability packaging:
IGBT Module Packaging
Diode and MOSFET Soldering
Power Semiconductor Assemblies
RF Device Packaging
High-reliability aerospace or automotive electronics
The effectiveness of formic acid in oxidation prevention has led to its integration in advanced vacuum reflow systems, such as those developed by companies like Chengliankaida Technology Co., Ltd., which specialize in semiconductor packaging solutions.
Safety and Handling Considerations
While formic acid is highly effective, its use must be handled with care:
It is corrosive and can be harmful if inhaled or contacted directly.
Industrial soldering systems using formic acid are typically enclosed and automated, with exhaust and neutralization systems in place.
Proper material selection for chamber components is essential to resist corrosion from acid vapor.
Automation and safety protocols mitigate most of these risks in modern equipment.
How Formic Acid Atmosphere Compares to Other Oxidation Prevention Methods
Formic acid provides a high-performance, low-residue solution without the need for high-temperature processing or reactive gases like hydrogen.
Future of Oxidation Prevention with Formic Acid
As the demands for miniaturization and reliability increase, oxidation prevention methods will continue evolving. The integration of formic acid into multi-zone vacuum reflow ovens and inline soldering systems enables precise control over temperature and atmosphere, making it scalable for high-throughput manufacturing.
In addition, ongoing research focuses on combining formic acid with plasma cleaning or laser-assisted heating to further enhance oxidation prevention and surface activation.
Challenges and Considerations When Using Formic Acid for Oxidation Prevention
While formic acid atmosphere has demonstrated exceptional effectiveness in oxidation prevention, it is important to consider certain technical and operational factors to ensure consistent outcomes:
1. Precise Process Control is Required
The efficiency of oxidation prevention with formic acid depends heavily on carefully controlled conditions—particularly temperature, formic acid concentration, and exposure time. If the temperature is too low, the reduction reaction may be incomplete. Conversely, excessive heat can lead to premature decomposition of formic acid, reducing its reducing power.
To ensure optimal oxide removal and solder joint integrity, advanced vacuum soldering systems must incorporate programmable temperature profiles and real-time gas flow control to maintain a stable formic acid environment.
2. Material Compatibility and Equipment Design
Because formic acid is mildly corrosive, the materials used in vacuum soldering systems—such as chamber walls, gas delivery lines, and sensors—must be resistant to acidic conditions. Materials like stainless steel (316L), PTFE, and certain ceramics are often used to ensure long-term durability.
In addition, the design of the chamber and gas distribution system plays a role in achieving uniform oxidation prevention across all components. Uneven distribution can lead to inconsistent oxide reduction, particularly on densely populated PCBs or complex multi-layer modules.
3. Monitoring Residue and Process Validation
Even though formic acid generates minimal residue compared to traditional fluxes, regular process validation and inspection are still essential. Some metal oxide combinations may form reaction by-products that condense under low vacuum, potentially interfering with optical components or chamber cleanliness.
Manufacturers often incorporate residue analysis, surface inspection (e.g., XPS or Auger spectroscopy), and bond pull/shear tests to validate that oxidation prevention has been fully effective and that solder joints meet required strength and reliability criteria.
The trend toward miniaturization, heterogeneous integration, and increased power density in modern electronic devices continues to drive the evolution of vacuum soldering systems. In this context, formic acid oxidation prevention plays a key role in enabling new packaging architectures.
Leading-edge vacuum soldering solutions now support features such as:
Multi-chamber inline reflow ovens with dedicated zones for preheating, formic acid exposure, soldering, and cooling.
Automated formic acid injection systems that optimize gas flow and minimize waste.
Real-time gas composition monitoring to ensure consistent oxidation prevention throughout production runs.
Process traceability software to track oxide removal efficiency and correlate it with device performance over time.
These advancements help support stringent industrial standards, including those required in automotive (AEC-Q100), military/aerospace, and medical electronics sectors, where oxidation prevention is critical for long-term reliability.
Updated Conclusion
Formic acid atmosphere has emerged as a powerful tool for oxidation prevention in reflow soldering, particularly when used in combination with vacuum soldering systems. Its chemical reduction capabilities enable the removal of metal oxides from critical surfaces, ensuring better solder wettability, fewer voids, and highly reliable interconnects in power and semiconductor devices.
With precise process control, compatible equipment design, and growing adoption in inline production systems, formic acid-based oxidation prevention is set to become a standard in advanced electronic packaging. As vacuum soldering technologies evolve, the synergy between atmosphere control and oxidation prevention will continue to enhance the quality, reliability, and scalability of modern electronics manufacturing.
Conclusion
Formic acid atmosphere provides an efficient and clean solution for oxidation prevention during
reflow soldering. Its effectiveness in reducing metal oxides, improving bond quality, and minimizing voids makes it an essential tool in semiconductor packaging and power device assembly. As more manufacturers adopt vacuum and formic acid-based processes, oxidation-related defects are expected to decrease significantly, leading to more reliable and efficient electronic components.

Comments