"What type of LED driver should I choose? Navigating through the multitude of options available for LED drivers can be quite challenging. There are numerous factors to consider when selecting the right one for your needs, which we comprehensively cover in our LED drivers guide here. One crucial decision is whether to opt for a constant current LED driver or a constant voltage LED driver. While LED drivers are commonly associated with constant current operation, manufacturers also provide constant voltage drivers for LEDs. Why is this the case? And how can we distinguish between these two types?"
Constant Current LED Drivers Vs. Constant Voltage LED Drivers
Both constant current and constant voltage drivers are suitable choices for powering LED light sources, but they differ in how they deliver power. LED drivers play a crucial role in supplying and controlling the power needed to ensure LEDs operate safely and reliably. Differentiating between these two types is essential for:
- Properly powering LEDs
- Preventing potential damage to your LED investment
Constant current LED drivers are specifically designed to provide a fixed output current (measured in mA or A) within a designated range of output voltages. LEDs that operate with constant current drivers require a consistent supply of current to ensure optimal performance. These drivers regulate voltage across the electronic circuit to keep the current stable throughout the LED system.
For instance,
Suncom’s Constant Current Driver exemplifies this approach:
Using higher current ratings can increase LED brightness, but without proper regulation, LEDs may draw more current than they are rated for. This condition, known as Thermal Runaway, leads to reduced LED lifespan and premature burnouts due to elevated temperatures. Constant current drivers are therefore essential for driving high-power LEDs, as they maintain uniform brightness and prevent issues across all LEDs connected in series.
What is a Constant Voltage LED Driver?
Constant voltage drivers are designed to provide a steady direct current (DC) output voltage, typically at 12VDC or 24VDC. LED lights that operate with constant voltage require a specific input voltage to function correctly, as indicated by their rating.
These drivers convert standard line voltage (120-277VAC), which is commonly found in household wall outlets, into a lower direct current voltage (VDC). Regardless of the current load applied, constant voltage drivers maintain a consistent voltage output.
For example, the LPV-60-12 driver ensures a stable 12VDC output, as long as the current remains below the maximum of 5 amps indicated in the specifications. Constant voltage drivers are commonly used in applications such as under-cabinet lighting and LED flex strip installations, although their versatility extends beyond these categories.
What Type of LED Driver Do I Need?
The case for constant current drivers:
When dealing with high-powered LEDs, a notable characteristic is the exponential relationship between the applied forward voltage and the resulting current flow. This phenomenon is clearly illustrated by the electrical characteristics of the Cree XP-G2 LED shown in Figure 1. Even a slight 5% increase in voltage (from 2.74V to 2.87V) can lead to a significant 100% rise in current through the XP-G2, as indicated by the red marks where current jumps from 350mA to 700mA.
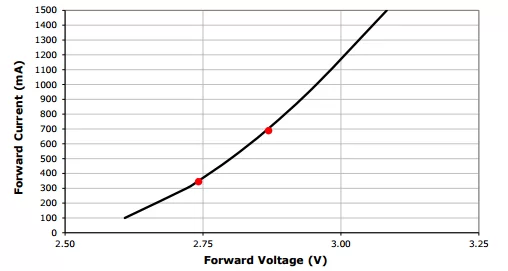
While higher current can indeed enhance LED brightness, it also risks over-driving the LED. Referencing Figure 2, which displays Cree’s specifications for maximum forward current and de-rating curves under various ambient temperatures, driving the XP-G2 LED at 700mA as seen in the example is within acceptable limits. However, without a current limiting device, changes in the LED’s electrical characteristics due to temperature fluctuations could cause it to draw excessive current. This scenario, particularly in warmer environments, could lead to thermal runaway—a condition where increased forward current generates excess heat, shortening the LED's lifespan and potentially causing failure.
To mitigate these risks, constant current LED drivers are preferred for powering high-powered LEDs. By maintaining a steady current output despite fluctuations in voltage caused by temperature changes, these drivers prevent over-driving of the LED and effectively mitigate thermal runaway.
When Should You Opt for a Constant Voltage LED Driver?
In real-world lighting applications, using individual high-powered LEDs as discussed earlier is often impractical and costly. Instead, manufacturers offer pre-assembled LED products such as LED rope lights, LED strips, and LED bars, which contain multiple LEDs arranged in series and/or parallel configurations.
Common LED strips, for instance, are typically designed with LEDs connected in series along with current-limiting resistors. These resistors are strategically placed to ensure stable operation regardless of minor fluctuations in the voltage supply, similar to what was described with the XP-G2 LED. Since the current is already regulated by these onboard resistors, these LED strips require only a constant voltage to power them.
When LEDs or LED arrays are configured in this manner, they are usually rated to operate at a specific voltage. For example, if your LED strip operates at 12VDC, you do not need to use a constant current driver; a 12VDC constant voltage source is sufficient. The built-in circuitry provided by the manufacturer ensures that the LEDs receive the correct current under varying operating conditions.
Benefits of Utilizing a Constant Current LED Driver
Therefore, when constructing your own fixture or working with high-powered LEDs, it is highly advantageous to use constant current drivers because:
- They prevent exceeding the maximum current specified for the LEDs, thereby preventing burnout or thermal runaway.
- They offer easier control for designers, ensuring more consistent brightness in the lighting application.
Benefits of Utilizing a Constant Voltage LED Driver
Constant voltage LED drivers are suitable when powering LEDs or arrays that require a specific voltage. This approach is advantageous because:
- Constant voltage technology is well-known and widely understood by design and installation engineers.
- These systems can be more cost-effective, especially in larger-scale applications.
Discover a dependable led driver today. Extensive inventory of led drivers. Class 1, 5-year warranties, and affordable power supplies ready to ship today!

Comments