When people think of "furniture," they often first imagine items like couches or chairs found in homes. However, furniture encompasses a wide variety of items that surround us daily. In residential settings, furniture includes dining room tables, end tables, bookcases, and large entertainment centers. In office environments, it extends to desks, conference room tables, office seating, and even mobile filing cabinets.
At
Gravity Caster, where we specialize in selling casters, our perspective on furniture revolves around its mobility. We ask the fundamental question: does the furniture move, or does it remain stationary? If mobility is required, then casters play a crucial role, and that's where our expertise comes into play. As authorized representatives for leading caster manufacturers, we are well equipped to assist you in selecting the best casters and wheels for mobile furniture applications.
7 Steps to Selecting a Caster
Selecting the right
casters and wheels for furniture involves navigating several critical considerations. Firstly, it's important to determine whether the casters need to complement the furniture's design or if they will be hidden from view. Additionally, understanding the type of flooring where the furniture will operate is crucial; for instance, carpeted floors typically require casters with rigid treads for better grip, whereas hard floors benefit from casters with softer treads to prevent damage and ensure smooth mobility.
Load capacity is another essential factor to evaluate. For example, with a table supported by four legs, each caster may only need to bear a quarter of the total weight. Conversely, for a four-legged chair, casters must be capable of supporting additional weight, especially if someone leans back on just two legs. In such cases, each caster should ideally handle at least half of the total load to ensure stability and durability over time.
Step 1 – Determine your product and mounting type.
Plate Type Swivel
Plate Type Fixed
With Leveling Mounts
Plug-in Type
Screw-In Type
Resin
With Shock Absorber
Angle Type
Step 2 – Determine your Load Capacity. The load capacity is determined by the formula below, safety factor and unevenness.
T = Required load capacity of one wheel or caster
E = Deadweight of the transport unit
Z = Maximum additional load
n = number of wheels or casters used
S = safety factor
The safety factor is determined by the speed and the ratio between wheel diameter and the height of obstacles. It is categorized into four distinct groups:
Indoor Manual Transport: For obstacles less than 5% of the wheel diameter, the safety factor ranges from 1.0 to 1.5.
Outdoor Manual Transport: For obstacles greater than 5% of the wheel diameter, the safety factor ranges from 1.5 to 2.2.
Indoor Power-Driven Transport: For obstacles less than 5% of the wheel diameter, the safety factor ranges from 1.4 to 2.0.
Outdoor Power-Driven Transport: The safety factor ranges from 2.0 to 3.0.
Step 3 – Select your Tread Material.
The hardness, shape, and tread material of wheels and casters significantly affect their operational comfort, smooth-rolling performance, and the resistance encountered during starting, rolling, and swiveling. Typically, the wheel tread or tire should be softer than the floor to prevent damage.
The flooring on which a wheel operates must withstand the pressure, particularly under high loads. Special attention is needed for floors made of wood, tar, concrete, or those that are electrically conductive to ensure they are not damaged and maintain their integrity.
Step 4 – Determine Maneuverability – Starting, rolling, and swivel resistance
The starting resistance is the force required to accelerate a loaded wheel from a stationary position to a moving one.
Rolling resistance is the force that must be overcome to keep a loaded wheel moving at a constant speed. This resistance is caused by the continuous compression and rebound of the tread during the rolling process, known as hysteresis, which leads to energy losses due to the internal friction of the material.
Factors affecting starting and rolling resistance include:
Wheel diameter
Load
Floor surface
Bearing type
Tread material
Swivel resistance is the force needed to change the direction of a swivel caster.
Factors influencing swivel resistance include:
Tread material
Contact surface (floor)
Offset
The maneuverability of a transport unit is determined by the number, type, and arrangement of the casters. These factors also impact the load capacity, mobility, guidance, turning circle, and stability of the vehicle.
Step 5 – Select the Bearing Type
The wheel bearing plays a crucial role in the rolling performance of a wheel and, by extension, the mobility of the application equipment. It must satisfy various requirements, including load capacity, operational duration, environmental conditions, starting and rolling resistance, as well as any additional specific criteria.
Plain Bore Bearing: The plain bore is a simple, cost-effective, and durable wheel bearing, corrosion-resistant, and maintenance-free under standard conditions.
Roller Bearing: The roller bearing is a sturdy, robust, largely maintenance-free wheel bearing type that only requires a small mounting space.
Central Ball Bearing: A central ball bearing offers a very precise, light running performance and a good sealing.
Step 6 – Consider Your Application’s Environmental Influence
When selecting
wheels or casters, it's crucial to consider their chemical resistance, particularly when these components come into direct contact with aggressive substances. Chemical resistance is influenced not only by the type of aggressive substance but also by factors such as its concentration, the duration of contact, and environmental conditions like temperature and humidity. These considerations are essential to ensure the durability and performance of the wheels or casters in challenging environments.
Step 7 – Additional Options and Requirements
Are you in need of locking mechanisms to control rolling or swiveling motions? Perhaps you require systems to lock or guide swivel movements?
Locking systems are essential for immobilizing casters during idle periods, preventing both rolling and swiveling motions.
Additionally, do you require brake systems?
Drum brakes utilize springs to maintain the braking state. Directional reset devices are employed to align swivel castors in specific orientations when unloaded.
If you are interested in
Gravity Caster's heavy duty swivel castors, feel free to send inquiries for pricing consultation. We will provide satisfactory quotations and services.
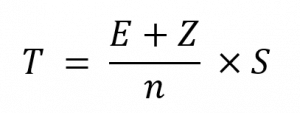
Comments