What Is Precision Soldering and Why Is It Crucial?
Precision soldering refers to the meticulous process of joining components using a controlled amount of heat and solder alloy to achieve high-quality, reliable electrical or thermal connections. It is a cornerstone of advanced manufacturing industries—semiconductors, aerospace, defense, and medical electronics—where component size is shrinking and performance requirements are increasing.
Unlike conventional soldering, precision soldering demands exact control over every variable—temperature, pressure, atmosphere, and timing—to ensure consistent and repeatable outcomes. Small errors can result in voids, delamination, or unreliable connections that compromise product life or function.
As semiconductor devices evolve toward miniaturization and higher power density, maintaining precision in soldering becomes essential for thermal performance and electrical efficiency.

What Is the Number One Rule of Precision Soldering?
The number one rule of precision soldering is temperature control.
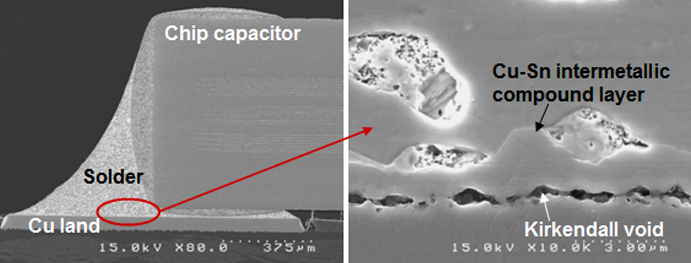
Temperature dictates the quality of every solder joint—it governs solder flow, wetting, intermetallic bonding, and the overall structural integrity of the connection. If temperature is too low, solder will not fully wet the surfaces, leading to cold joints and high resistance. If it’s too high, components and substrates can be damaged, or intermetallic layers can grow excessively, weakening the bond.
In short, precise thermal control ensures solder joints that are uniform, clean, and durable. This rule is universal across all forms of precision soldering—manual micro-soldering, reflow soldering, vacuum soldering, and laser-based joining techniques.
How Temperature Control Defines the Quality of Soldering
Every stage of precision soldering—preheating, soaking, reflow, and cooling—depends on stable temperature profiles. Here’s how it affects joint integrity:
- Wetting Behavior: Proper temperature ensures that solder melts completely and spreads evenly across the surfaces.
- Intermetallic Formation: Controlled heating creates the ideal thickness of intermetallic layers, ensuring strong metallurgical bonds.
- Void Reduction: Gradual temperature ramps prevent gas entrapment and void formation within the joint.
- Component Protection: Sensitive components like MOSFETs or ICs can suffer from thermal shock if the heating or cooling rate is too rapid.
Modern systems employ multi-zone thermal control, where each zone precisely regulates heat using real-time feedback sensors and software algorithms. This technology minimizes variation and ensures reproducibility.
What Equipment Enables Precision Soldering?
Precision soldering relies on sophisticated equipment capable of maintaining tight process tolerances. Common types include:
- Vacuum Reflow Ovens: Remove air pockets and gases, minimizing void rates and ensuring hermetic sealing.
- Hot-Bar and Pulse Heating Systems: Deliver localized heat precisely to joints without damaging nearby areas.
- Laser Soldering Machines: Provide pinpoint accuracy for microelectronic and optical component assembly.
- Intelligent Control Systems: Utilize sensors, AI algorithms, and programmable profiles to monitor every thermal cycle.
Chengliankaida Technology Co., Ltd. has contributed to innovations in this area through R&D of vacuum soldering systems that control both temperature and pressure simultaneously, ensuring high-reliability joints for semiconductor packaging.
Why Cleanliness Is the Second Rule of Precision Soldering
If temperature is the number one rule, cleanliness is undoubtedly the second.
Contaminants—oil, oxide, dust, or moisture—can severely affect solder adhesion and cause weak or intermittent joints. The smallest residue on a bonding pad can prevent wetting and lead to open circuits.
Best practices for cleanliness include:
- Using isopropyl alcohol (IPA) for pre-cleaning components.
- Employing no-clean fluxes or inert atmospheres to reduce residue.
- Storing materials in humidity-controlled environments.
In high-end manufacturing, precision soldering often takes place under nitrogen or vacuum conditions to eliminate oxidation entirely.
How Flux Enhances Soldering Precision
Flux plays a critical role in precision soldering. It removes oxides and prevents new ones from forming during heating, promoting smooth solder flow. The type of flux chosen depends on the application:
- Rosin-based flux: For general electronics.
- No-clean flux: Leaves minimal residue, suitable for semiconductors.
- Water-soluble flux: Requires post-cleaning but ensures strong wetting.
Incorrect flux or overuse can cause corrosion, ionic contamination, or short circuits. Therefore, precise flux application and compatibility testing are vital to every precision soldering process.
How Do Solder Alloys Impact Precision and Reliability?
Material selection is another pillar of precision soldering. Each alloy behaves differently under thermal stress:
- Tin-Lead (Sn-Pb): Traditional choice with low melting point but restricted due to RoHS compliance.
- Lead-Free Alloys (Sn-Ag-Cu): Commonly used in modern electronics; requires higher temperatures.
- Gold-Tin (Au-Sn): Offers exceptional strength and hermeticity, ideal for power devices and aerospace.
- Silver-Based Alloys: Used where thermal conductivity and joint strength are critical.
Precision soldering demands exact temperature matching to the alloy’s melting range to ensure complete wetting without damaging parts.
What Are the Common Defects and Their Causes in Precision Soldering?
Defects are often a result of violating the golden rule—poor temperature control or unclean conditions. Common defects include:
- Cold Joints: Caused by insufficient heat.
- Bridging: Excess solder connecting adjacent pads.
- Voids: Gas trapped within the joint during soldering.
- Delamination: Inadequate surface preparation or contamination.
- Non-wetting: Improper flux or oxidized surfaces.
These issues can be mitigated by controlling the temperature profile, ensuring flux activity, and maintaining component cleanliness throughout production.
How Does Atmosphere Influence Precision Soldering?
The soldering environment plays a significant role in joint quality:
- Air Atmosphere: Standard, but oxidation risk is higher.
- Nitrogen Atmosphere: Reduces oxidation, improves wetting and joint appearance.
- Vacuum Soldering: Eliminates gas inclusions, ensuring low void ratios and hermetic sealing.
Vacuum-assisted precision soldering is increasingly adopted in power semiconductor packaging, providing unmatched reliability and performance.
How to Achieve Repeatability in Precision Soldering?
Repeatability means achieving identical results every cycle. In high-tech industries, it’s essential for quality assurance. Methods include:
- Defining standard temperature profiles.
- Automating solder paste deposition and reflow control.
- Using closed-loop feedback systems.
- Implementing process monitoring and traceability.
Statistical process control (SPC) helps detect deviations early, reducing defects and improving yield rates.
What Safety Measures Support Precision Soldering Operations?
While precision soldering deals with small-scale components, safety remains paramount:
- Use fume extraction to remove flux vapors.
- Wear ESD protection to prevent static discharge.
- Handle hot tools with thermal gloves.
- Maintain equipment regularly to prevent overheating.
- Adhering to safety protocols ensures both operator well-being and consistent process reliability.
What Are the Key Applications of Precision Soldering?
Precision soldering is indispensable across industries:
- Semiconductor Packaging: For IGBT, MOSFET, and LED modules requiring hermetic joints.
- Aerospace and Defense: For vibration-resistant and temperature-stable connections.
- Medical Devices: For high-reliability sensors and imaging components.
- Automotive Electronics: For electric vehicles and battery management systems.
By mastering precision soldering, manufacturers can achieve the high quality demanded by these critical sectors.
How Automation Enhances the Precision Soldering Process
Automation improves consistency and throughput by eliminating human variability. Robotic systems and AI-driven temperature controllers adjust parameters dynamically in response to sensor data.
Machine vision systems inspect solder joints in real time, ensuring each one meets microscopic standards. Automated data logging enhances traceability, a vital factor in industries like semiconductor and aerospace manufacturing.
How Does Research and Development Shape the Future of Soldering?
Continuous research is driving innovation in soldering materials, equipment, and control algorithms. New technologies like laser precision soldering and AI-integrated vacuum soldering systems enable higher accuracy and lower defect rates.
Chengliankaida Technology Co., Ltd. has worked alongside universities and industry alliances to advance soldering processes for semiconductor devices, focusing on reducing void rates and improving hermetic packaging performance.
What Trends Will Define the Future of Precision Soldering?
The coming decade will witness revolutionary trends:
- Smart Manufacturing: Integration of IoT for real-time monitoring.
- Miniaturization: Handling components smaller than 0.2 mm with micron-level accuracy.
- Eco-Friendly Processes: Lead-free alloys and energy-efficient ovens.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Using analytics to predict maintenance and prevent process failures.
The precision soldering industry is evolving toward full automation, intelligence, and sustainability.
Conclusion: Why the Number One Rule Will Never Change
Temperature control remains the number one rule of precision soldering—a timeless truth that underpins every successful joint. No matter how advanced materials and machines become, maintaining thermal consistency will always be the key to quality and reliability.
From the smallest microchip to the largest power module, precision soldering ensures connectivity, performance, and durability. Engineers who master this discipline uphold the integrity of the modern electronic world.